Disposal
Objectives and steps in nuclear waste management
For the management of radioactive waste – they arise in the course of nuclear power, but also in medicine, industry and research – under Swiss legislation (in the nuclear energy act and radiation protection act) there is a regulation that radioactive waste is to be disposed of locally and in such a way that the long-term protection of people and the environment is ensured.
Based on current, globally recognised knowledge, emplacement in deep geological repositories is the only method for the disposal of radioactive waste which also meets the high requirements for long-term safety. Concepts whose safety relies on constant monitoring by humans do not meet these requirements for the long-time periods required. Federal council and parliament have selected the concept of a geological deep repository for this reason.
(see https://www.admin.ch/opc/de/federal-gazette/2001/2665.pdf)
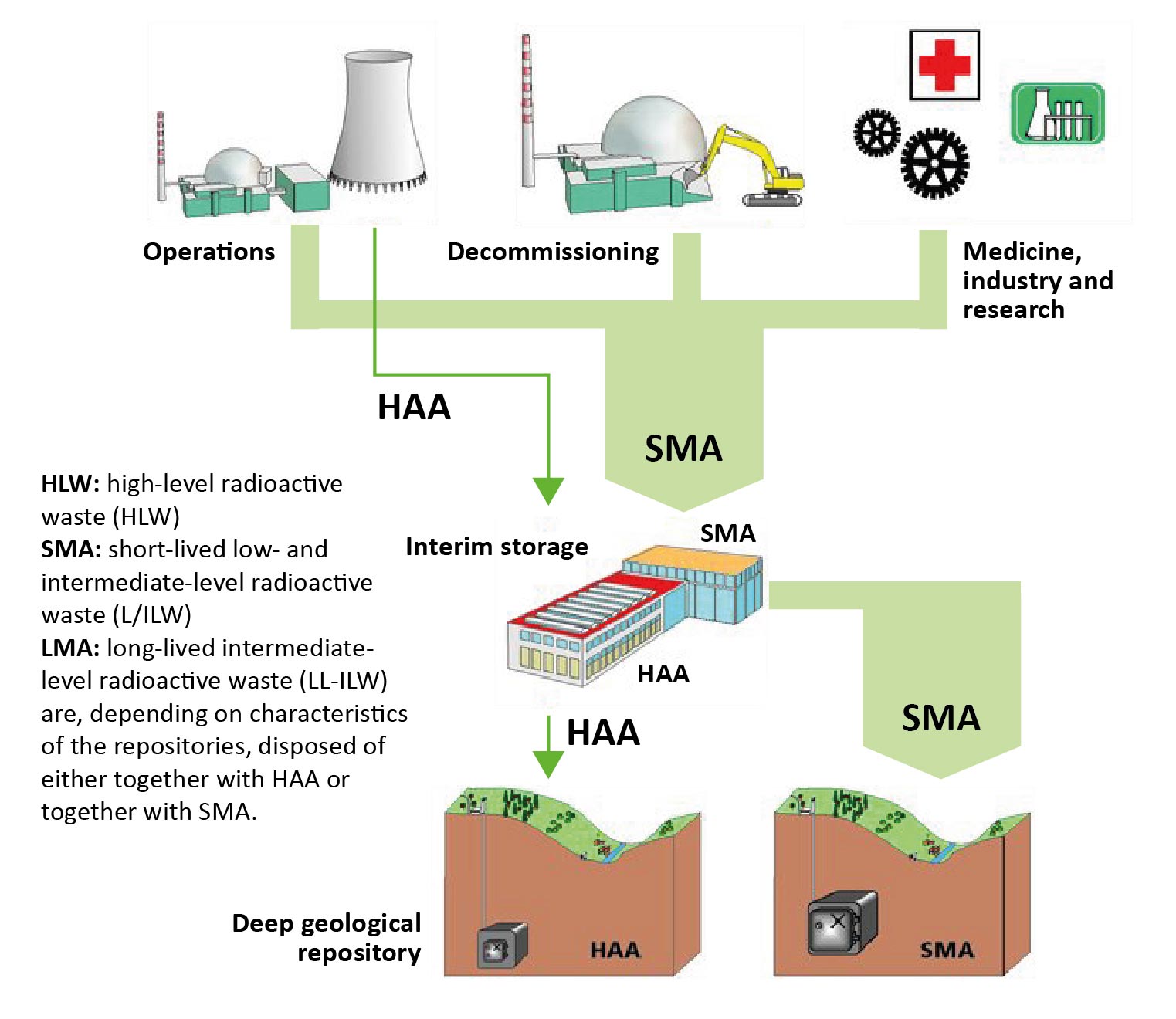
Radioactive wastes arise during the operation and decommissioning of nuclear power plants as well as in medicine, industry and research. They are stored in interim storage and later transferred to deep geological repositories. Source: www.ensi.ch
A geological deep repository will only be available in Switzerland in the second half of our century. Until then the radioactive waste will be retained in interim storage.
So that the radioactive waste can be stored and later transferred to geological deep repository, it must be conditioned, i.e. treated and packed in such a way that it will not require any further waste treatment in the future.
Therefore, the disposal of radioactive waste comprises conditioning, interim storage and emplacement in a deep geological repository. An important aspect of handling radioactive waste as part of these waste disposal steps is transport, both facility-internal and on public transport routes.